
How AI Ensures Compliance with Moderation Laws
AI moderation tools are transforming how platforms manage harmful content, ensuring compliance with strict regulations like the EU Digital Services Act (DSA), GDPR, and evolving U.S. state laws. Here's the big picture:
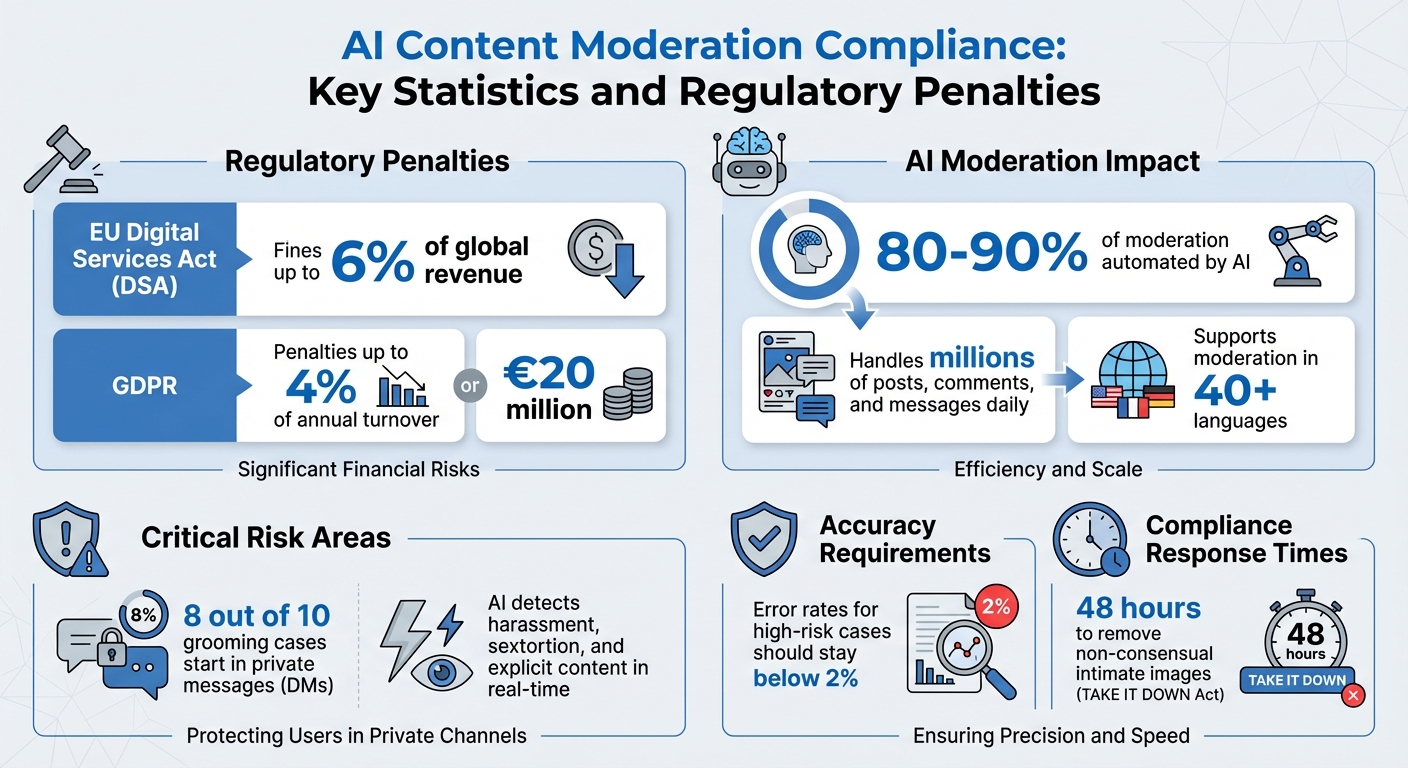
- Fines for non-compliance can reach up to 6% of global revenue under the DSA or 4% under GDPR.
- AI automates 80–90% of moderation, handling millions of posts, comments, and messages daily.
- Private messaging is a critical risk area, with 8 out of 10 grooming cases starting in DMs. AI tools can detect harassment, sextortion, and explicit content in real-time.
- Human oversight remains essential to handle nuanced decisions, appeals, and to meet transparency requirements.
AI tools like Guardii.ai go beyond basic moderation by managing Instagram comments and DMs in over 40 languages, auto-hiding toxic content, and generating audit-ready evidence packs for legal compliance. This mix of automation and human review helps platforms reduce legal risks, protect users, and maintain trust.
In this guide, we’ll explore how AI-driven moderation tackles compliance challenges, reduces exposure to penalties, and supports safer online communities.
AI Content Moderation Compliance: Key Statistics and Regulatory Penalties
Can AI solve content moderation and regulatory compliance for platforms in 2023?
Regional Moderation Laws and Their Impact
Navigating regional moderation laws is a challenging task for organizations operating across borders. In the European Union, regulations like the Digital Services Act (DSA) and the EU AI Act enforce strict compliance measures, often accompanied by severe penalties. Meanwhile, in the United States, Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act offers broad legal protections, though state-level laws are beginning to chip away at these safeguards. Understanding these varying rules is essential - not just to avoid fines, but to create moderation systems that work effectively across different legal landscapes. Let’s dive into how these laws differ in the EU and the U.S.
Digital Services Act (DSA): EU Requirements
The DSA places a heavy emphasis on transparency and accountability. Platforms must offer user-friendly reporting tools, provide clear explanations for content removals, and establish effective appeal processes. Failure to comply with these rules can lead to fines as high as 6% of a company’s global annual revenue.
When platforms use automated moderation tools, the DSA mandates full disclosure of these systems in both their terms of service and transparency reports. These reports must also detail error rates and system limitations. For Very Large Online Platforms (VLOPs), the requirements are even tougher. They must conduct systemic risk assessments to identify potential issues like disinformation, threats to fundamental rights, or risks to minors. These assessments must include actionable risk mitigation plans and provide accredited researchers with access to relevant data. For industries like sports, entertainment, and brand management, keeping detailed logs of every moderation decision is particularly critical.
Adding to this, the EU AI Act introduces a risk-based framework, categorizing AI systems by their potential hazards. High-risk systems used in content moderation must maintain detailed technical documentation, demonstrate accuracy and reliability, and ensure human oversight for decisions that could affect fundamental rights. This is especially important for handling sensitive content, such as political speech, satire, or news, where automated moderation alone could jeopardize freedom of expression.
Now, let’s shift gears to the U.S., where the legal environment takes a different approach.
Section 230 and US State-Level Laws
Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act is a cornerstone of U.S. internet law. Section 230(c)(1) shields platforms from liability for user-generated content, while Section 230(c)(2) offers additional protection for platforms that remove harmful material in good faith. This legal framework has allowed U.S.-based platforms to scale AI moderation systems without being held accountable for every single post that remains online.
However, state and federal laws are evolving to address new challenges. For instance, the TAKE IT DOWN Act focuses on removing non-consensual intimate images and AI-generated deepfakes. Platforms must act within 48 hours of receiving a valid request, with the FTC enforcing compliance. Additionally, state legislatures have introduced a wide range of AI-related bills, tackling issues like transparency and youth safety. This creates a fragmented legal landscape, requiring platforms to adapt their moderation practices to meet varying state-level requirements.
For companies serving global audiences, these regional differences demand tailored compliance strategies. AI tools can be configured with jurisdiction-specific rules, such as stricter takedown policies and detailed documentation for EU users, while allowing for broader speech protections in the U.S.. Tools that generate audit logs and evidence packs - used by sports organizations and influencers to document threats or harassment - are becoming indispensable for demonstrating good-faith enforcement to regulators, sponsors, and legal advisors.
How AI Tools Enable Compliance
AI moderation systems have become a cornerstone for meeting legal requirements on a large scale. With platforms managing millions of content interactions daily, manual review alone can't keep up with regulatory demands. AI tools step in by scanning content in real time, flagging violations, and generating necessary documentation - all while easing the workload of human teams. This automation allows platforms to shift from a reactive approach to a more proactive one, addressing issues before they escalate.
The move toward proactive moderation is largely influenced by regulations like the Digital Services Act (DSA) and various U.S. state laws, which require platforms to mitigate risks before harm occurs. AI makes this shift possible by detecting violations automatically, routing high-risk content to human reviewers, and maintaining audit trails to show compliance efforts. For organizations that engage with global audiences - such as sports teams, influencers, journalists, and brands - these capabilities are essential for staying ahead of regulatory expectations.
Automated Filtering and Risk Assessment
AI-powered filtering systems analyze text, images, and videos to swiftly identify harmful or illegal content. These systems use machine learning to detect inappropriate language, explicit imagery, and patterns that indicate threats or harassment, flagging violations immediately. Platforms can then auto-hide or remove such content before it spreads to a wider audience.
This approach directly aligns with laws that impose severe penalties for non-compliance. For example, under the DSA, platforms risk fines of up to 6% of global revenue for failing to act, while GDPR violations can cost up to 4% of annual turnover. By automating content filtering, organizations not only reduce exposure to illegal material but also minimize the financial and reputational risks tied to regulatory failures.
Risk assessment tools further enhance compliance by scoring content and user behavior to gauge the likelihood of violations. AI can spot early signs of harassment, fraud, or coordinated abuse by analyzing activity patterns. High-risk cases are then prioritized for human review, allowing legal and safety teams to focus on the most urgent threats.
AI also helps platforms navigate jurisdiction-specific rules. For instance, a platform operating in both the EU and U.S. can configure its AI to enforce stricter takedown policies for EU users while respecting broader speech protections under Section 230 in the U.S. This kind of localization is key for managing the complex and fragmented legal landscape, especially as U.S. states introduce new laws on deepfakes, AI-generated CSAM, and child safety.
Multilingual Threat Detection and DM Moderation
AI moderation tools go beyond filtering by addressing language barriers to ensure comprehensive global moderation. Threats and harassment can occur in any language, and AI systems capable of supporting over 40 languages ensure harmful content is detected consistently, regardless of the user’s language. These tools analyze sentiment, context, and linguistic nuances to identify hate speech, threats, and covert harassment across different languages.
Private messaging (DM) moderation is another critical area for compliance. Studies show that eight out of ten grooming cases begin in private messaging channels, and platforms are increasingly held accountable for failing to detect and prevent abuse in these spaces. AI tools use pattern recognition and natural language processing to identify explicit images (like cyberflashing), threatening language, and sexualized harassment in DMs. When a potential threat is detected, the system can auto-hide the message, quarantine it for review, and generate evidence packs to meet legal requirements.
For public figures, influencers, and sports organizations, these capabilities are especially important. Take Guardii, for example - a platform that moderates Instagram comments and DMs in over 40 languages. It auto-hides toxic comments in line with Meta's policies and detects DM threats and harassment. The system prioritizes cases, alerts teams through familiar channels, and provides audit logs and evidence packs. These features are invaluable for organizations facing scrutiny from sponsors, legal advisors, or regulators.
AI also lightens the load for safety teams by handling routine cases. It flags obvious violations and auto-hides harmful content, leaving only ambiguous or high-stakes cases for human reviewers. This hybrid approach ensures that nuanced decisions receive the necessary human oversight, balancing compliance with the protection of free expression.
Implementing AI for Compliance and Protection
To effectively implement AI moderation tools, organizations need to align legal requirements with their operational processes. This means translating complex regulations into actionable system settings, like determining what content should be automatically hidden, what requires human review, who gets notified, and how evidence is stored. The aim is to create a moderation system where every decision is logged, transparent, and defensible in front of regulators or courts.
With structured AI governance now requiring detailed documentation, algorithms are increasingly treated as accountable entities. This means liability may hinge on how an AI system ranks, amplifies, or suppresses content - not just on what users post. To minimize legal risks, it’s crucial to implement transparent and well-documented processes. Building on earlier discussions about automated risk assessments, it’s essential to configure systems to log, review, and justify every moderation decision. Let’s explore how to set up auto-hide features and priority alerts to enhance compliance.
Setting Up Auto-Hide and Quarantine Queues
Auto-hide features are a frontline defense against harmful content. They work by scanning content in real time using AI models tailored to both platform policies and legal standards. These systems can immediately conceal blatantly illegal or harmful material - like explicit threats, hate speech, or graphic violence - before it spreads to a broader audience.
To strengthen your defenses, establish clear thresholds for auto-hiding high-risk content while quarantining borderline cases. For example, high-confidence violations, such as direct death threats or child safety concerns, should be auto-hidden immediately. Meanwhile, ambiguous cases - like satire, reclaimed language, or news content - should be routed to quarantine queues for human review. This hybrid approach balances AI’s capabilities with the need for nuanced, context-aware decisions, meeting the responsiveness regulators demand.
Quarantine queues should prioritize content based on risk and exposure. For instance, threats to life, targeted harassment of vulnerable groups, or posts from high-profile accounts should be reviewed first. Each flagged item in the queue should include vital context, such as conversation threads, user history, language details, model confidence scores, and the specific policy rule that was triggered. This ensures consistent and defensible decisions while maintaining the documentation trail required by laws like the Digital Services Act.
Take Instagram moderation as an example. Its tools can auto-hide harmful comments in over 40 languages while routing direct message threats or sexualized harassment into quarantine. Organizations can set severity thresholds to auto-hide high-risk content and quarantine medium-risk material, with all actions timestamped and documented. This reduces exposure and supports legal defenses with audit-ready logs.
Using Priority Alerts and Evidence Workflows
Beyond content filtering, real-time alerts and evidence workflows add another layer of compliance and protection. Priority alerts ensure that critical incidents don’t get buried in moderation queues. AI can be configured to send notifications for urgent issues, such as credible threats, doxxing, or coordinated harassment. Clear escalation paths - like directing violent threats against athletes to security teams or flagging sensitive content for brand protection - help streamline responses.
Alerts should include key details, such as a content snippet, confidence level, triggered policy, user context, and recommended next steps. This enables teams to quickly gauge the severity of an incident and decide whether to escalate to law enforcement, preserve evidence, or take immediate action on the platform. Integrating alerts into tools like Slack, Teams, or email ensures they reach the right people without requiring constant dashboard monitoring.
Evidence workflows are equally critical. Every moderation decision should produce concise logs that serve as audit trails and legal defenses. These logs demonstrate compliance to regulators and provide documentation for litigation when needed.
For example, Guardii’s evidence packs automatically compile flagged content, detection metadata, and moderator notes into downloadable reports. Such documentation is crucial for meeting reporting requirements under frameworks like the DSA or defending claims under Section 230.
sbb-itb-47c24b3
Ensuring Accuracy and Reporting
As AI systems become central to content moderation, ensuring accuracy through detailed reporting and audit logs is no longer optional - it's a regulatory necessity. Platforms must provide clear documentation to prove compliance, showing exactly how their AI systems enforce moderation policies with transparent logs, metrics, and evidence trails.
The stakes are high. Under the DSA, fines can climb to 6% of global revenue, while GDPR penalties may reach €20 million or 4% of annual turnover. In the U.S., Section 230 protections are under increasing scrutiny, particularly in cases involving algorithmic amplification or suppression. Legal experts have observed a sharp rise in lawsuits targeting platforms for how their AI ranks and prioritizes content.
Generating Audit-Ready Logs for Regulators
Every decision made by a moderation system should leave behind a complete, timestamped record. These audit logs are not only critical for internal accountability but also serve as a key defense during regulatory investigations or legal disputes. Effective logs capture vital metadata such as content identifiers, timestamps, detection methods, policy triggers, and flags for human review. To ensure integrity, logs must be tamper-proof and access-controlled.
For compliance with the DSA, logs should include detailed reasons for content removal and offer users a way to contest those decisions. Similarly, New York law mandates large platforms to submit compliance reports every six months. To meet these demands, logging systems should automatically generate reports - quarterly or biannual - summarizing metrics like the volume of content reviewed, detection channels, types of actions taken (e.g., removal or reduced visibility), median response times, and appeal outcomes across different jurisdictions.
Guardii exemplifies this approach by compiling flagged content, detection metadata, and moderator notes into downloadable reports. These reports align with DSA and GDPR requirements, offering both compliance assurance and protection against liability claims.
Beyond regulatory needs, robust logging also plays a crucial role in refining AI models, enabling continuous improvement in precision and effectiveness.
Tuning AI Systems for Precision
Accuracy in content moderation isn't just about user satisfaction - it’s a compliance requirement. Mistakenly removing content can infringe on free expression, while failing to catch harmful material can lead to enforcement actions or lawsuits. Regulatory frameworks like the EU AI Act and DSA explicitly require risk assessments, high-quality datasets, and documented testing for high-risk AI systems.
Tracking error metrics, such as false positives and negatives, is essential. For high-risk cases, these rates should stay below 2%. Platforms need to monitor error rates by policy type, language, and geography, focusing on areas where mistakes carry higher legal or reputational risks - such as hate speech, child safety, or direct threats.
Fine-tuning AI systems requires a combination of continuous feedback and controlled testing. Techniques like A/B testing, phased rollouts, and ongoing monitoring are crucial for maintaining compliance. Guardii’s platform illustrates this with smart filtering that goes beyond basic keyword matching, reducing false alarms while accurately identifying harmful content. Its adaptive learning system incorporates human feedback from review queues, allowing moderators to handle edge cases and refine the AI’s performance. This hybrid approach - where borderline or high-impact cases are flagged for human review - enhances both accuracy and compliance.
Maintaining a detailed register of all AI models used in moderation is equally important. This should include information on each model’s purpose, training data sources, known limitations, evaluation dates, and ownership. Version control for moderation policies and tracking updates helps correlate enforcement patterns with changes in policies or models, demonstrating a proactive and responsible approach to managing AI systems.
Adapting to Changing Moderation Laws
Once compliance measures are firmly in place, the next challenge is staying ahead of ever-changing content moderation laws. Regulations like the EU's Digital Services Act (DSA), GDPR, a mix of U.S. state-level AI laws, and the evolving interpretations of Section 230 require platforms to regularly update their systems. These updates are essential to meet new demands for transparency, appeals, and accountability. Falling behind isn't just risky - it’s expensive. Under the DSA, fines can reach up to 6% of global revenue, while GDPR violations can cost up to 4% of global revenue.
Courts are also expanding their focus. It’s no longer just about what users post, but also how platforms rank, amplify, or suppress content using AI moderation. This shifting legal landscape calls for a thoughtful balance between automated systems and human oversight.
Combining AI with Human Review
AI is incredibly effective at handling large-scale, first-line moderation tasks. It can quickly identify clear violations like hate speech, threats, spam, and other obvious policy breaches. However, when it comes to more nuanced or context-sensitive cases, human judgment is indispensable. Regulations increasingly require human oversight to ensure that automated decisions aren’t final and can be challenged or overridden.
To make this work, it’s crucial to define roles clearly. AI should handle straightforward cases with high confidence, while ambiguous or context-heavy content - like politically sensitive speech or borderline harassment - should be flagged for human review. Human moderators can then focus on these edge cases, manage user appeals, audit AI decisions for bias, and refine moderation policies as legal standards evolve. This balanced approach not only minimizes legal risks but also helps maintain user trust and supports free expression.
Take Guardii as an example. The platform uses AI to monitor Instagram comments and DMs in over 40 languages, flagging content for human review through Priority and Quarantine queues. Human teams can override AI decisions, tweak detection thresholds, and compile detailed evidence packs and audit logs. These tools are especially valuable when responding to regulatory inquiries or resolving user disputes.
Creating Playbooks for Regulatory Updates
A well-prepared regulatory updates playbook is essential for systematically addressing new legal requirements. This playbook should outline who is responsible for tracking legal changes, how to interpret new obligations - such as transparency reporting, appeal timelines, and notification standards - and how these map to content rules and AI system configurations. It should also include steps for effective communication, such as internal briefings, updates to public policies, and user notifications. Timelines for implementing changes and validating them through audits or external reviews should also be part of the process. Together, these practices strengthen compliance and support the audit and reporting procedures already in place.
Maintaining region-specific policies within AI systems and moderator workflows is equally important. For instance, EU users under the DSA may require stricter notice-and-appeal processes, while U.S. state laws might demand different transparency or bias-audit measures. Tools that allow for modular policy adjustments make it easier to adapt rules by region without needing to rebuild AI models entirely.
To keep the playbook effective, update it regularly with version control and assign clear ownership. Training human moderators and safety teams on the legal context behind each update is just as critical. Using decision trees for common edge cases and region-specific scenarios helps ensure consistent enforcement. This structured, proactive approach not only keeps your moderation systems compliant but also demonstrates to regulators that your organization is serious about staying ahead of legal requirements.
Conclusion
Staying compliant is not optional. With the ever-changing landscape of U.S. state-level laws creating a maze of regulations, organizations need scalable solutions that ensure both accuracy and clarity. AI-powered tools are stepping up to this challenge, filtering harmful content in real-time, identifying threats in multiple languages, and generating the detailed, audit-ready documentation that regulators require.
Take Guardii, for example. This tool showcases how AI can directly support sports clubs, athletes, influencers, and journalists managing Instagram communities. It automatically hides toxic comments, identifies threatening direct messages in over 40 languages, and flags risky content for further review. On top of that, it provides evidence packs and detailed audit logs - resources that safety teams and legal departments can rely on to prove compliance and address regulatory demands effectively.
Successful moderation relies on a combination of technology and human judgment. AI handles large-scale filtering, but human oversight ensures sensitive cases and appeals are handled with care. This balanced approach reduces false positives, protects reputations, and ensures that moderation decisions hold up under regulatory scrutiny.
As discussed earlier, blending real-time AI filtering with focused human review creates a strong foundation for compliance. Organizations that prioritize AI systems with robust governance will be better positioned to adapt to shifting moderation laws. Features like automated filtering, multilingual threat detection, customizable thresholds, and thorough audit trails establish a reliable moderation framework that safeguards both users and the organization.
Proactive moderation goes beyond avoiding penalties - it’s about cultivating safer online environments. By making this protection scalable and regulation-ready, organizations empower athletes, creators, and communities to connect without fear of abuse, even as regulatory demands continue to evolve.
FAQs
How does AI help platforms follow regional content moderation laws?
AI significantly aids platforms in meeting regional content moderation laws by analyzing and interpreting content across various languages and cultural settings. It automates the process of identifying and removing harmful or non-compliant material, ensuring platforms align with local regulations while prioritizing user safety.
These systems can also highlight questionable content for human review, minimizing errors like false positives or negatives. On top of that, AI supports legal and safety teams by providing detailed evidence logs and streamlined audit workflows, helping organizations maintain accountability and safeguard their communities more effectively.
Why is human oversight important in AI-powered content moderation?
Human involvement is essential for making AI-driven content moderation accurate, fair, and sensitive to context. While AI can handle massive amounts of data and detect patterns quickly, humans bring the nuanced understanding needed to navigate complex situations, like ensuring legal compliance or addressing safety concerns.
When humans review flagged content, they help refine AI systems by reducing false positives (wrongly blocking acceptable content) and false negatives (overlooking harmful material). This teamwork ensures moderation decisions meet ethical guidelines and comply with local regulations, resulting in a safer and more dependable experience for users.
How do AI tools detect and manage threats in private messages?
AI tools leverage advanced algorithms to scan private messages in real-time, spotting harmful content like threats or instances of sexual harassment. When such content is identified, the system can either quarantine it immediately or flag it for review by safety or legal teams.
This swift response plays a key role in creating a safer space by tackling toxic behavior as it happens, while also preserving evidence to support accountability and meet moderation regulations.