
How AI Detects Anomalies in Social Media Messages
AI is transforming how social media platforms handle harmful content, especially for athletes, influencers, and brands. With millions of comments and messages exchanged daily, manual moderation is no longer feasible. AI anomaly detection steps in to flag threats, harassment, and unusual behaviors before they escalate. Here's what you need to know:
- What qualifies as an anomaly? Sudden spikes in negative sentiment, threatening language, or unusual behavior like bots posting hostile comments.
- Why it matters: Online grooming cases have surged 400% since 2020, with 80% starting in private messages. AI helps detect these early to protect users and reputations.
- How it works: AI uses unsupervised learning (like clustering and autoencoders) to spot outliers and supervised models (like BERT) to classify threats across 40+ languages.
- Key features: Sentiment shifts, keyword analysis, timing patterns, and multilingual moderation ensure harmful content is flagged while reducing false positives.
AI systems like Guardii.ai also provide evidence packs and audit logs, helping legal teams respond quickly. While challenges like bias and slang interpretation remain, combining automation with human oversight makes AI a powerful tool for safer online spaces.
Moderating AI and Moderating with AI (RSM Speaker Series)
AI Techniques for Detecting Anomalies
AI systems combine unsupervised methods to identify unusual patterns and supervised models to classify specific threats. Together, these tools power real-time moderation systems that help safeguard athletes, creators, and families from harm.
Unsupervised Learning for Identifying Outliers
Unsupervised methods excel at spotting content that strays from typical patterns, even as those patterns shift over time. Techniques like clustering algorithms - such as DBSCAN and K-means - group similar messages and flag those that fall outside the usual clusters. For instance, DBSCAN can detect density-based anomalies, such as coordinated hate speech campaigns or sudden bursts of bot-like activity, all without needing pre-labeled data.
Isolation forests take a different approach by partitioning features like posting frequency, sentiment, and word choice to isolate outliers. Similarly, autoencoders - neural networks designed to compress and reconstruct data - learn what "normal" content looks like. When they encounter something unusual, like threatening metaphors or grooming language, the reconstruction error spikes, triggering an alert. These methods are particularly useful for spotting new attack strategies, evolving slang, or even individual deviations in behavior.
Once these outliers are flagged, supervised models step in to classify the specific nature of the threat.
Supervised Learning for Threat Classification
After anomalies are identified, supervised models classify the exact type of threat. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks analyze message sequences to detect patterns of escalating harassment. Transformer-based models like BERT are especially effective at identifying subtle threats, often achieving F1-scores above 0.80.
These models are trained on datasets meticulously labeled with examples of hate speech, sexual harassment, violent threats, and other harmful behaviors. Platforms like Guardii.ai, for example, use multilingual BERT variants to classify threats in over 40 languages. This allows them to identify issues ranging from sexualized harassment in private messages to coordinated attacks in public comment sections. By categorizing threats clearly, these systems enable quick and targeted moderation.
What AI Looks for in Social Media Messages
AI has become a powerful tool in identifying potential threats within social media interactions. By analyzing messages at a granular level, it can detect signs of danger by focusing on two main aspects: the content of the message - such as the words used and the emotional tone - and the behavioral context, which includes timing and patterns of communication. Let’s break down how these signals are identified and used to monitor social media messages effectively.
Sentiment Shifts and Keyword Analysis
One of the key ways AI detects threats is by monitoring shifts in emotional tone. For example, if a user's messages suddenly change from friendly to aggressive, such as saying, "You're going down after the game", the system flags this as a potential warning sign of harassment. Similarly, when an influencer’s direct messages shift from being complimentary to sexually explicit, AI detects the inconsistency by comparing the new messages with the sender’s usual communication style.
AI doesn’t stop at analyzing mood - it also evaluates keywords in context. Instead of relying on simple profanity filters, modern systems look at clusters of words to identify slurs, violent language, or sexualized content. This approach helps reduce false alarms by considering the context in which the words are used. For example, predators often use coded language that seems innocent at first glance but follows recognizable patterns, particularly in grooming scenarios. By understanding metaphors, slang, and humor, AI can distinguish between a heated argument and genuine harassment.
Timing and Interaction Patterns
AI also examines the timing and patterns of interactions to identify unusual behavior. For instance, messages sent at odd hours - like 3 AM - or sudden spikes in activity may indicate bot behavior or obsessive harassment. By analyzing a user’s normal communication rhythm, the system can quickly detect irregularities, such as a flood of hostile messages targeting someone during unusual times.
Patterns in interactions can also reveal coordinated attacks. For example, AI identifies abnormal reply chains where one user dominates with increasingly hostile comments or detects bot accounts working together to launch group attacks. If a creator suddenly receives a surge of messages from multiple accounts, the system flags this as a potential issue and prioritizes these messages for review. This is especially critical in private messaging, where research shows that 8 out of 10 grooming cases begin.
Platforms like Guardii.ai take these techniques a step further by combining content and behavioral analysis. Supporting over 40 languages, Guardii.ai can monitor communications in real-time, identifying and mitigating threats while minimizing false positives. This ensures a safer online environment for users across different languages and regions.
How Anomaly Detection Works in Social Media Moderation
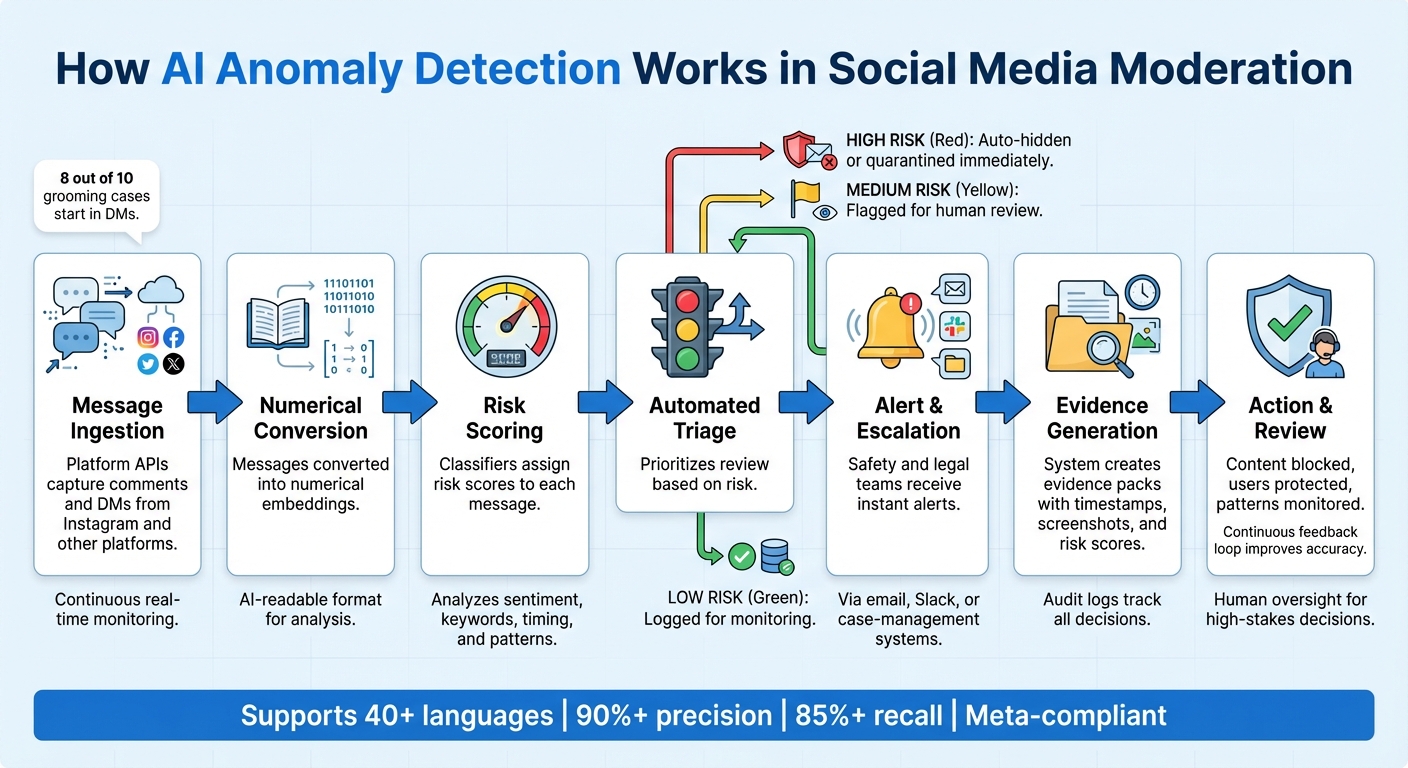
How AI Detects Anomalies in Social Media Messages: A Step-by-Step Process
AI-powered anomaly detection is changing the game for platforms like Instagram, helping them protect users by continuously analyzing incoming comments and direct messages through platform APIs. Here’s how it works: messages are converted into numerical embeddings, which are then scored by classifiers. High-risk messages - those above a certain threshold - are automatically hidden or quarantined. Medium-risk ones are flagged for human review, while low-risk messages are simply logged. This system keeps moderation teams focused on the most pressing threats without requiring them to sift through every single message. By analyzing individual messages, the groundwork is laid to identify broader patterns over time.
But it doesn’t stop there. The system also tracks behavior over time, spotting potential threats like a sudden surge in abusive comments or repeated targeting of an individual, such as an athlete. When these patterns emerge, the AI sends alerts to safety and legal teams, enabling swift action, whether that’s blocking offenders or escalating the issue further.
Detecting Threats in 40+ Languages
Multilingual moderation relies on transformer-based models fine-tuned on datasets covering abusive language in multiple languages. These models use subword tokenization and shared vocabularies, allowing a single system to understand semantics across more than 40 languages. They can even handle slang, spelling variations, and code-switching.
The process starts with identifying the dominant language of each message. Once identified, the message is routed to the appropriate classifier or multilingual model. Special adaptations are in place for unique scripts, like right-to-left languages or non-Latin alphabets. For example, if an American sports team competes in a European tournament, the system can detect and quarantine hostile messages written in local languages before they ever reach the athlete - even if the moderation team doesn’t speak those languages. Similarly, influencers with diverse audiences spanning the United States, Latin America, and Europe can rely on the system to catch harmful direct messages, such as sexualized language or threats, without the need for manual translations or user reports.
Platforms like Guardii.ai integrate these multilingual models with region-specific rules, ensuring consistent moderation across all languages and dialects. This approach not only supports brand safety but also helps organizations meet regulatory standards in international markets.
Minimizing False Positives
One of the biggest challenges in automated moderation is separating genuine threats from harmless banter. To tackle this, systems create dynamic allow-lists and pattern rules that account for the intense language often found in sports and fandoms - like chants or rivalry nicknames - that don’t usually signal real harm.
To refine this process, models are trained on domain-specific data, such as historical comments from particular leagues or teams. This training enables the system to differentiate between ritualized trash talk and credible threats, such as explicit harm, doxxing, or persistent harassment. Human reviewers also play a vital role by correcting over-blocked content, feeding their corrections back into the system for continuous improvement. Over time, the AI becomes better at allowing contextually appropriate language while flagging messages that mix rivalry talk with harmful elements like hate slurs or threats of violence.
Moderation teams often use configurations tailored to specific sports or leagues, regularly reviewing samples of auto-hidden content to fine-tune allow-lists while maintaining safety. The system combines outputs from multiple models into a composite risk score, which is then calibrated to align with real-world probabilities. Safety teams can adjust thresholds based on the context - for example, applying stricter settings for minors, women athletes, or high-risk journalists, while being more lenient in lower-risk scenarios. Performance metrics are continuously monitored to strike a balance, ensuring critical threats are flagged without overwhelming teams with false positives.
Protecting Women Athletes and Creators from Sexual Harassment
Detecting sexual harassment involves using text classifiers trained on data that identifies sexualized language, coercion, grooming, and non-consensual requests. These are paired with computer vision models capable of identifying nudity or explicit imagery in attached media. For issues like cyberflashing, image classifiers and hashing-based systems flag explicit content, while unusual behaviors - like a surge in new accounts sending explicit images - trigger additional alerts.
Research highlights that 8 out of 10 grooming incidents begin in private direct messages, making DM monitoring a critical part of user safety. For women athletes and creators, high-severity harassment cases are routed to specialized queues where trained staff follow clear guidelines. These include immediate actions like blocking or muting offenders, preserving evidence, and providing sensitive communication to the affected individual. In more serious cases, issues are escalated to platform safety teams or law enforcement.
Platforms like Guardii.ai also create structured evidence packs that include timestamps (formatted as MM/DD/YYYY in U.S. standards), message content, screenshots, and model scores. These detailed reports support legal and safety measures. Additionally, audit logs track every moderation decision, allowing wellbeing teams and psychologists to monitor abuse trends and implement targeted interventions. This not only helps protect users but also demonstrates to stakeholders that moderation efforts are active, measured, and effective.
sbb-itb-47c24b3
Building Anomaly Detection into Moderation Workflows
AI has become an essential part of moderation workflows, acting as a first line of defense that processes content in real time, assesses risks, and escalates only the most urgent cases for human review. This approach ensures moderation teams can focus on genuine threats instead of wading through an overwhelming volume of routine content.
The system analyzes text, images, and even behavioral patterns - like sudden spikes in comments or the emergence of suspicious accounts - to assign severity scores. High-risk anomalies trigger instant alerts via tools like email, Slack, or internal case-management systems, enabling teams to act within minutes. Meanwhile, less critical content is queued for later review, and benign material is automatically archived. Below, we’ll explore how automated queues, evidence packs, and secure data storage fit into this workflow.
Automated Priority Queues for Harmful Messages
AI categorizes incoming messages into different queues based on their severity. The most critical issues - such as credible threats, doxxing, severe harassment, or coordinated attacks - are routed to Priority queues, where trust and safety teams operate under strict response protocols. Lower-severity or ambiguous items are placed in Quarantine queues for batch review, significantly reducing the volume of content moderators need to handle.
For instance, if an Instagram DM contains sexual harassment, the system flags it, routes it to a high-priority queue, and alerts safety teams immediately. In scenarios like sports organizations, repeated threats against an athlete can reach legal teams in minutes, while less severe cases are quarantined for review at a later time.
Evidence Packs and Audit Logs
Once messages are prioritized, the system generates detailed evidence packs. These packs include everything needed for further action, such as the original message, screenshots, U.S.-formatted timestamps, user IDs, language details, and any associated media. They also provide model outputs like risk scores, detected categories (e.g., "threat of violence" or "sexual harassment"), confidence levels, and details about the rules that were triggered. This information helps legal teams by offering a clear, unbiased record that can be used as evidence in court.
Audit logs complement these evidence packs by tracking every action taken in the system. For example, logs document changes like when content is hidden, appealed, or reinstated, along with timestamps, the responsible party (AI, moderator, or admin), and the reasoning behind each decision. These tamper-proof records are invaluable for regulatory audits and help demonstrate that moderation processes are thorough and consistent. They also allow teams to monitor abuse trends, identify repeat offenders, and develop targeted interventions - providing assurance to sponsors and partners that moderation efforts are effective.
Meta-Compliant Moderation and Data Storage
For smooth integration into existing workflows, moderation systems must align with Meta's guidelines. This means toxic comments are typically hidden instead of being outright deleted unless reported, and users must have the ability to appeal moderation decisions. AI workflows follow these rules by applying Meta-approved filters, using platform APIs to hide harmful content from public view while preserving it for review, and logging all actions to prevent penalties. This "quarantine" approach minimizes harm while maintaining due process.
Data storage and retention are also critical. For U.S.-based organizations, data is usually stored in U.S. data centers to comply with regulations like the CCPA. However, organizations operating in the EU or other regions may need to use local storage solutions. Retention periods can vary depending on the type of data - for example, routine operational data might be kept for 30–90 days, while high-risk evidence tied to legal cases could be stored for one to three years. Platforms like Guardii.ai offer region-specific hosting and strong encryption to ensure sensitive data remains secure and compliant with Meta’s terms for data use and storage. This reduces legal risks and ensures that moderation practices meet regulatory standards.
Measuring AI Anomaly Detection Performance
Once AI anomaly detection becomes part of moderation workflows, it’s crucial to measure how well it performs. Teams need clarity on whether the system is effectively identifying genuine threats without overwhelming moderators with unnecessary alerts. This evaluation hinges on specific metrics that help determine how accurately the AI separates harmful content from normal activity. These metrics form the foundation for ongoing performance monitoring in the context of social media moderation.
Precision, Recall, and F1-Score
Three key metrics are used to gauge performance: precision, recall, and F1-score.
- Precision measures how many flagged messages are genuinely harmful. It’s calculated as True Positives divided by (True Positives + False Positives). High precision is essential because it ensures moderators spend less time reviewing harmless content. For example, if the system has 92% precision, it means 92 out of every 100 flagged messages are actual threats.
- Recall, also known as sensitivity, measures the proportion of real threats the AI successfully identifies. It’s calculated as True Positives divided by (True Positives + False Negatives). Strong recall is critical to avoid missing harmful content, such as instances of sexual harassment in private messages. If there are 100 harmful messages, and the AI identifies 87 of them, the recall rate is 87%.
- The F1-score combines precision and recall into a single number by calculating their harmonic mean: 2 × (Precision × Recall) / (Precision + Recall). This metric is particularly useful in moderation scenarios where harmful content is rare - often less than 1% of total messages. To balance efficiency and safety, production systems typically aim for precision above 90%, recall above 85%, and F1-scores above 0.87.
Different AI models excel in different areas. LSTM models are strong at analyzing sequential patterns, such as message timing, while BERT and other transformer-based models outperform LSTMs when it comes to understanding context, sentiment, and slang. For example, BERT-based models often achieve F1-scores between 0.92 and 0.95 for text-based threats, outperforming LSTMs by 5–10% in natural language processing tasks. In multilingual moderation systems that handle over 40 languages, fine-tuned BERT models can maintain 91% precision and 87% recall, even when dealing with cultural idioms, ensuring fewer false positives while still catching harmful content.
Weekly KPI Dashboards
To provide a broader operational perspective, moderation teams rely on weekly KPI dashboards. These dashboards track key metrics such as precision, recall, F1-score, false positive rates, and detection volume. They help identify trends - like a sudden 15% drop in recall, which could indicate model drift and the need for retraining. Alerts are triggered when performance thresholds are breached, allowing teams to respond quickly.
In addition to model metrics, these dashboards focus on operational outcomes that directly impact user safety and brand reputation. For example, teams monitor how many messages are moderated per 1,000 posts and aim for 95% compliance with platform rules.
For platforms like Guardii.ai, which moderates Instagram comments and DMs across 40+ languages, dashboards break down metrics by language and harm category - such as threats, hate speech, or sexual harassment. Performance can vary greatly between languages, so precision, recall, and F1-scores are displayed separately for each. Other tracked metrics include priority queue latency (how quickly high-risk messages are escalated), evidence pack generation rates, and the percentage of AI decisions overridden by human moderators. For instance, logs from a weekly review of 100 cases might show a 92% F1-score, with 8% of AI decisions overridden due to slang misinterpretation. These insights guide targeted improvements to the model.
Conclusion: AI's Role in Social Media Safety
AI-powered anomaly detection is playing a growing role in keeping users and reputations safe across social media platforms. By scanning messages for harmful content - such as hate speech, bullying, and coordinated harassment - these systems can step in early to prevent harm from escalating. For women athletes and creators, who often experience higher levels of sexual harassment through private messages that bypass public moderation, AI serves as a vital defense by automatically isolating abusive content before it reaches them.
On a broader scale, AI also helps protect the reputations of organizations. Sports teams, media outlets, and brands can now block toxic comments during high-stakes moments, preserving their public image. Tools like Guardii.ai offer features such as multilingual detection across over 40 languages, Meta-compliant auto-hiding, and Priority/Quarantine queues. These tools also include audit logs, which support safety, legal, and wellbeing teams in the United States.
That said, there are still hurdles to overcome. AI models can unintentionally embed biases, struggle with minority dialects, and misinterpret subtleties like sarcasm or reclaimed language - issues that disproportionately affect marginalized groups. To address these challenges, human oversight is essential for high-stakes decisions. Regular audits that evaluate performance across different demographics and languages, along with transparent feedback systems, can help refine these models. Additionally, organizations should clearly communicate how AI is being used, limit data storage to what’s absolutely necessary, and give creators control over their filtering settings to ensure they retain autonomy over their online spaces.
Tracking performance metrics is key to finding the right balance between automation and human review. Weekly dashboards that measure precision, recall, flagged content volume, and reviewer response times allow teams to evaluate whether AI is effectively reducing exposure to harmful content while lightening the workload for moderators. When precision exceeds 90% and recall hits 85% or higher, teams can confidently address risks without overwhelming moderators. By combining automation with human oversight, AI anomaly detection offers a scalable and practical approach to enhancing social media safety for the future.
FAQs
How does AI identify threats while ignoring harmless comments on social media?
AI works to spot threats by examining the context, tone, and patterns in social media posts. It looks at things like specific word choices, how phrases are structured, and recurring behaviors to identify harmful intentions, such as threats or harassment, while steering clear of mistaking casual or innocent remarks for dangerous ones.
By using sophisticated algorithms, AI can pick up on subtle differences in language. This helps cut down on false alarms while ensuring that truly concerning content is flagged for further review. The goal is to strike a balance between keeping people safe and allowing open, free-flowing conversations.
Why is human oversight important in AI moderation systems?
Human oversight is a key component of AI moderation systems, ensuring they operate with both precision and fairness. While AI is excellent at processing massive amounts of social media content to flag harmful behavior, it occasionally stumbles when faced with subtle nuances. Context, sarcasm, cultural variations, or ambiguous language are areas where AI might misjudge, leading to errors like false positives. This is where human moderators step in, using their judgment to assess these complex cases.
The combination of AI’s speed and human insight creates a more balanced approach to moderation. It helps maintain a careful equilibrium between safety, privacy, and ethical concerns. Additionally, this partnership allows AI algorithms to improve over time, keeping them in sync with changing legal frameworks and societal expectations.
How does AI detect threats in social media messages across different languages and cultures?
AI has the ability to spot threats in social media messages by examining patterns, flagging suspicious behavior, and interpreting context across different languages and cultural settings. Using advanced algorithms, it navigates linguistic challenges and cultural subtleties to ensure precise detection while minimizing false alarms.
This skill plays an important role in moderating content in multilingual spaces, shielding users from harmful interactions, and fostering a safer, more welcoming online environment.