
AI Moderation: Personalized Federated Learning Explained
Personalized federated learning (PFL) is reshaping how AI handles online abuse by tailoring moderation systems to individual users while keeping their data private. Unlike one-size-fits-all models, PFL creates custom AI models for each user, improving accuracy in detecting harmful content like harassment, threats, and hate speech. It trains locally on user devices and only shares model updates - not raw data - with a central server, ensuring privacy.
Key takeaways:
- Athlete Safety: Auto-hide toxic comments without hurting fan engagement or sponsor trust.
- DM Threat Detection: Identify and document harassment in under 15 minutes.
- False Positives: Allow rivalry slang (e.g., Hindi, Tamil) without flagging harmless banter.
- Women Creators: Manage sexualized harassment and cyberflashing with legal-ready evidence.
- Sponsor Protection: Keep social channels safe during high-profile events like match days.
- Multilingual Moderation: Handle content in 40+ languages with reduced errors.
- Evidence & Compliance: Provide audit-ready documentation for abusive comments and DMs.
- Metrics That Matter: Track moderation success with precision, recall, and creator retention.
PFL ensures moderation systems are both effective and privacy-focused, making it a game-changer for athletes, influencers, and brands navigating the challenges of online abuse.
On Privacy and Personalization in Federated Learning (Flower AI Summit 2024)
How Personalized Federated Learning Works
Personalized federated learning creates customized models for individual users while leveraging shared insights across a network. Instead of centralizing raw data, this system trains models directly on user devices and only transfers model updates to a central server. This ensures sensitive information, such as private messages or comment histories, remains secure and decentralized.
What makes this approach stand out is its ability to balance shared learning with individual customization. A global model identifies common patterns - like widely recognized markers of toxic language - while each user's model adapts to their specific context. This combination of shared insights and local adjustments is what allows the system to handle diverse data effectively.
Handling Data Differences and Model Customization
One of the biggest challenges in federated learning is dealing with the wide variety of user data. For instance, in content moderation, users encounter unique language styles and harassment patterns. A traditional global model, trained on averaged data, often struggles to address such diversity.
Personalized federated learning addresses this with advanced customization techniques that maintain global knowledge while adapting locally. For example, global knowledge distillation ensures essential universal patterns - like common signs of harmful behavior - are preserved during local training. At the same time, methods like Learn2pFed assign weights to model parameters, determining which aspects should remain global and which can specialize. Research shows these techniques improve accuracy in environments with diverse data. Once local models are fine-tuned, the next step is selecting the right clients for aggregation.
Client Selection and Model Aggregation
Choosing the right clients is crucial for efficient training and managing system variability. In traditional federated learning, one slow client can delay the entire process. Personalized systems tackle this with smarter client selection methods. For example, reinforcement learning can prioritize clients based on the quality of their data and training speed. FedPRL, for instance, uses a multi-layer perceptron to evaluate potential participants, focusing on those with representative data and faster training capabilities. This approach reduces communication rounds and speeds up training while ensuring the system remains accurate and responsive.
After local training, clients share only their model parameters - not their raw data - with a central server. The server combines these updates using weighted averaging, factoring in the amount of local data each client contributes. Unlike traditional federated learning, which produces a single global model, personalized systems allow clients to further refine their models. This might involve fine-tuning with local data or blending global predictions with local adjustments, ensuring the final model better suits individual needs.
Traditional vs. Personalized Federated Learning
Traditional federated learning aggregates client updates into a single global model, assuming data across users is relatively uniform. While this can work for simpler tasks, it often struggles with diverse data, leading to inconsistent performance across users. Personalized federated learning, on the other hand, tailors models to individual users, improving accuracy by 5–15% in settings with varied data. Though personalized systems require more complex algorithms and higher local computation, the benefits are clear - especially in tasks like AI moderation. This precision helps reduce false positives and negatives, which is critical for maintaining real-time moderation accuracy.
Using Personalized Federated Learning for AI Moderation
Personalized federated learning (PFL) is reshaping AI moderation by crafting context-aware models without the need to centralize sensitive data. Instead of applying the same moderation standards across athletes, influencers, or brands, PFL tailors models to differentiate harmful content from acceptable community interactions.
Let’s explore how PFL brings practical improvements to content moderation.
Adaptive Content Moderation for Athlete Safety
Athletes face unique challenges when it comes to online interactions. What might seem like harmless fan banter can sometimes cross the line into harassment. PFL addresses this by training a global model on common toxicity markers - such as hate speech, threats, and slurs - and then fine-tuning it locally to account for individual contexts.
For example, a sports club could use this approach to automatically hide toxic Instagram comments while still encouraging positive fan engagement. Tools like FedPRL have achieved an 18% boost in accuracy by focusing on high-quality data from accounts experiencing active abuse. These systems can hide up to 95% of harmful content, effectively distinguishing genuine threats from routine trash talk.
Companies like Guardii.ai are already applying this method, offering moderation tools for sports clubs and athletes. Their system auto-hides toxic content in real time while prioritizing urgent threats and flagging borderline cases for review by safety teams. This ensures a balance between automated efficiency and human oversight, especially in diverse linguistic settings.
Multilingual Moderation and Reducing False Positives
Moderating content in over 40 languages comes with its own set of challenges. Slang, code-switching, and culturally specific expressions can trip up traditional moderation systems. A phrase that’s offensive in one language might be harmless in another.
PFL tackles this by adapting models to local language nuances. Using adaptive regularization techniques, it balances global toxicity markers with local slang and expressions, cutting false positives by 10–20% in complex environments. By fine-tuning models on diverse datasets locally and then aggregating them globally, PFL ensures strong multilingual performance while keeping sensitive data decentralized.
Real-Time DM Threat Detection and Legal Support
Private messages pose a high-stakes challenge for moderation. Threats, doxxing, sexualized harassment, and grooming attempts often occur in private conversations, making real-time detection critical. PFL enables this by training personalized models on edge devices, which process local data and send only gradient updates to a central server. This setup allows the system to flag high-risk behaviors - such as explicit threats, attempts to move conversations off-platform, or requests for personal information - with response times under 100 milliseconds.
Once a threat is identified, the system compiles evidence packs that combine global predictions with locally stored data. These packs include timestamps, message context, and risk scores, creating verifiable records that meet legal and compliance standards. For sports organizations, this means they can document harassment patterns, track repeat offenders, and maintain audit logs that satisfy sponsors and regulatory requirements.
Guardii.ai’s DM threat detection system works within this framework, identifying threats and harassment in over 40 languages. It generates detailed evidence packs for legal and safety teams, tracks repeat offenders, and sends alerts through platforms like Slack, Teams, or email. This allows human oversight where it’s most needed, while automated processes handle the heavy lifting of managing large-scale data efficiently.
sbb-itb-47c24b3
Deploying Personalized Federated Learning in Moderation Systems
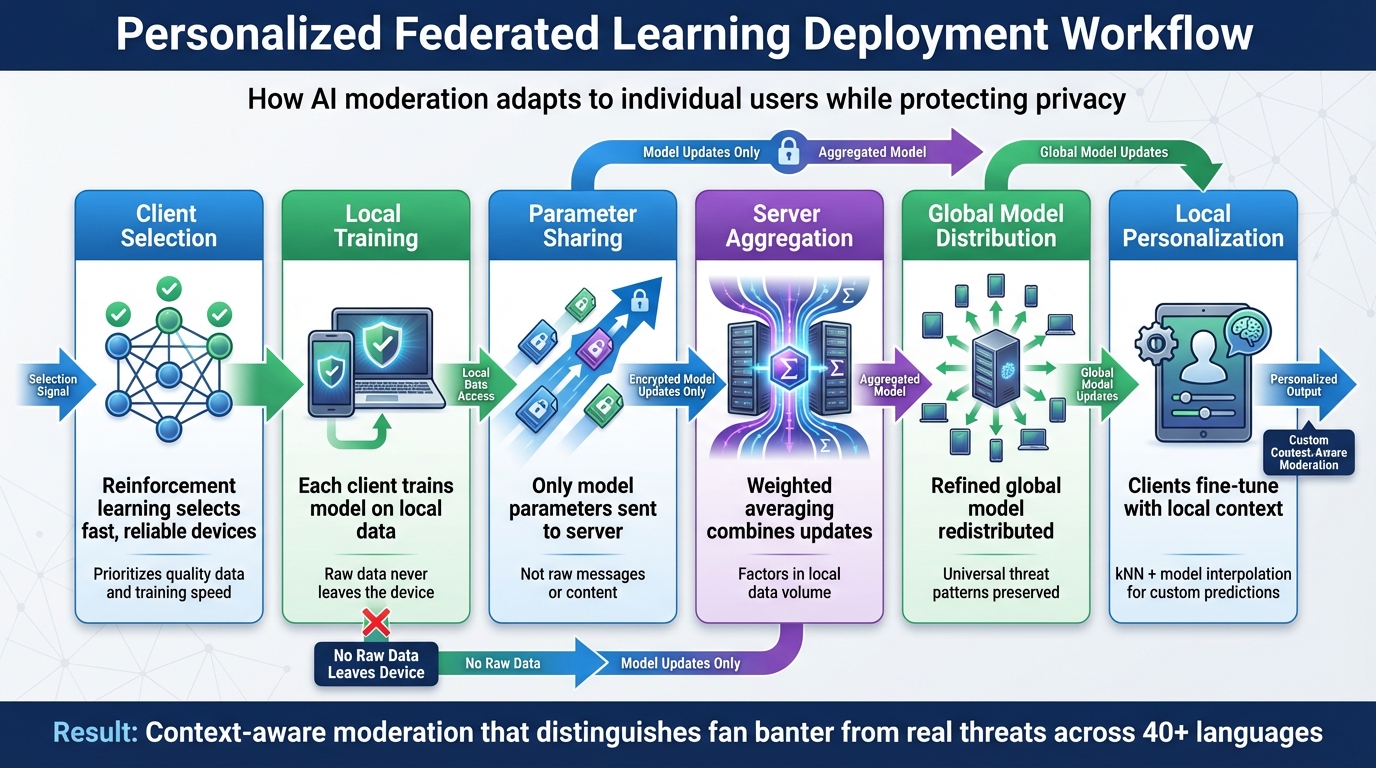
How Personalized Federated Learning Works: 6-Step Deployment Process
Implementing personalized federated learning creates a moderation system that respects privacy while adapting to specific needs. For sports organizations and influencers, turning this concept into a deployable solution requires a clear and structured approach.
Step-by-Step Workflow
The deployment process transforms the principles of personalized federated learning into a scalable, practical system. This involves six key stages, starting with reinforcement learning to select clients. By prioritizing fast and reliable devices, the system avoids delays and ensures smooth operation.
Each client trains a model locally using its own data, sharing only the model parameters - not the raw data - with the server. The server then aggregates these updates through weighted averaging and redistributes the refined global model. Clients further personalize this global model using their local data and techniques like k-nearest neighbors (kNN) and model interpolation. This approach allows the system to make context-specific predictions, such as distinguishing between playful fan banter and legitimate threats aimed at an athlete. Additionally, global knowledge distillation ensures the system retains universal threat-recognition patterns while adapting to local nuances, maintaining a balance between personalization and general threat awareness.
Scaling and Communication Efficiency
Once the foundational workflow is established, scalability becomes the next priority. Techniques such as model compression and adaptive optimization help manage communication across a wide range of devices. Dynamic aggregation further enhances efficiency by adjusting resource allocation based on the capabilities of each client, preventing systems from overloading when handling high-traffic accounts.
In practice, this means a sports organization can deploy moderation tools across mobile devices, desktops, and server-side proxies without consuming excessive bandwidth. For instance, platforms like Guardii.ai efficiently moderate comments in over 40 languages, managing thousands of interactions simultaneously.
Privacy and Compliance Requirements
Privacy is a cornerstone of federated learning, as only model updates - not raw data - are sent to the central server. To ensure additional security, differential privacy introduces noise to these updates, making it impossible to reverse-engineer individual contributions. Secure multi-party computation further protects the aggregation process, ensuring data remains confidential.
From a compliance standpoint, this system aligns with GDPR's data minimization principles by avoiding centralized storage of personal data. Local auto-hide mechanisms meet Meta's policies, while audit logs are generated from aggregated insights rather than raw messages. When legal teams require evidence for harassment cases, the system compiles detailed records, including timestamps, message contexts, and risk scores, all sourced from local storage. This ensures verifiable documentation without compromising user privacy. These measures provide a balance between legal compliance and user trust, safeguarding athlete privacy while meeting the needs of sponsors and regulatory bodies.
The Future of Personalized Federated Learning in AI Moderation
Personalized federated learning is poised to transform how AI safeguards creators in online spaces. Unlike traditional global models that apply uniform rules to every account, this technology enables countless customized models. These models adapt to local abuse patterns while benefiting from shared knowledge across the network. For athletes and influencers, moderation filters can be fine-tuned to reflect personal boundaries and audience expectations - all without exposing raw messages. This evolution offers a moderation approach that is both adaptable and privacy-conscious.
Benefits for Athletes, Influencers, and Brands
Personalized models can adjust moderation intensity during critical periods, such as game days, playoffs, or major product launches. Athletes, for instance, can set specific thresholds for what they consider unacceptable - whether it’s appearance-based insults, racial slurs, or threats to their family. The system learns from their feedback, creating a tailored experience. Brands also stand to benefit. Filters can be customized to suit different industries: a children’s brand might enforce strict controls on inappropriate content, while a fashion account could allow edgy language but block hate speech entirely.
This approach is already being implemented. Instead of sharing raw content, only model updates are exchanged, enabling organizations to pool insights across teams while maintaining privacy and adhering to Meta compliance standards. This system not only protects creators from harmful content but also safeguards brand reputations with audit logs that document moderation efforts.
Measuring Success with Key Metrics
To measure the effectiveness of personalized federated learning, organizations can monitor specific metrics. Precision (the percentage of flagged content that is genuinely abusive) and recall (the percentage of actual abuse that is successfully identified) are essential benchmarks. These metrics can be evaluated across different groups - such as women athletes versus men, or English speakers versus Spanish speakers - to ensure the system serves diverse communities without introducing bias.
Beyond these technical metrics, broader indicators like abuse exposure rate (average number of abusive comments seen by a creator daily), escalation accuracy (how well critical content is prioritized), and creator retention (changes in posting habits after improved moderation) are crucial. Additionally, tracking moderation costs per account and monitoring brand safety incidents can help verify whether these systems provide tangible benefits in terms of safety and reputation. These metrics will guide future improvements and innovations.
Future Developments and Trends
Looking ahead, advancements in personalized federated learning will further refine moderation systems to align with individual risk profiles while enhancing privacy. Emerging meta-learning techniques will allow models to adapt specific parameters for each account while leveraging a strong global framework. Reinforcement learning will optimize training by focusing on accounts with high-quality, representative abusive content.
Multimodal approaches will expand capabilities to detect harassment in various forms - whether through text, images, or videos. This could include identifying harmful memes, gestures, or altered images. On-device personalization will also become more prevalent, enabling lightweight models to filter content directly on users’ devices. Only encrypted, aggregated updates will be shared with servers, preserving privacy.
As U.S. privacy laws and platform accountability standards continue to evolve, these data-minimizing architectures will be critical. They’ll not only help meet regulatory requirements but also build and maintain trust with creators and users alike.
FAQs
How does personalized federated learning protect user privacy in AI moderation?
Personalized federated learning takes a privacy-first approach by training AI models directly on users' devices. Instead of sending raw data to a central server, it shares only anonymized or aggregated updates. This ensures that sensitive information remains safely on the device.
By keeping data private, this method not only protects personal information but also fine-tunes AI moderation. It adapts models to individual contexts while maintaining strict security and confidentiality standards.
How does personalized federated learning improve multilingual content moderation?
Personalized federated learning takes multilingual content moderation to the next level by enabling AI models to adjust to the specific linguistic and cultural subtleties of various communities. This fine-tuning significantly reduces false positives and negatives, ensuring a more precise identification of harmful content across multiple languages.
What makes this approach even more compelling is its focus on user privacy. The models are trained directly on local devices or servers, eliminating the need to share sensitive data. This method not only improves moderation accuracy but also meets strict privacy requirements, making it a strong choice for environments that demand both precision and confidentiality.
How does personalized federated learning enhance threat detection in private messages?
Personalized federated learning takes threat detection to the next level by tailoring AI models to match individual user behavior and communication patterns directly on their devices. This fine-tuning allows the system to spot potential threats with greater precision, cutting down on both false alarms and missed detections.
What makes this approach stand out is its ability to process data locally. By keeping data on the user’s device, it not only protects privacy but also ensures the AI continues to learn and adapt. This is particularly useful for detecting harmful content in private messages as it happens, creating safer and more secure communication spaces.